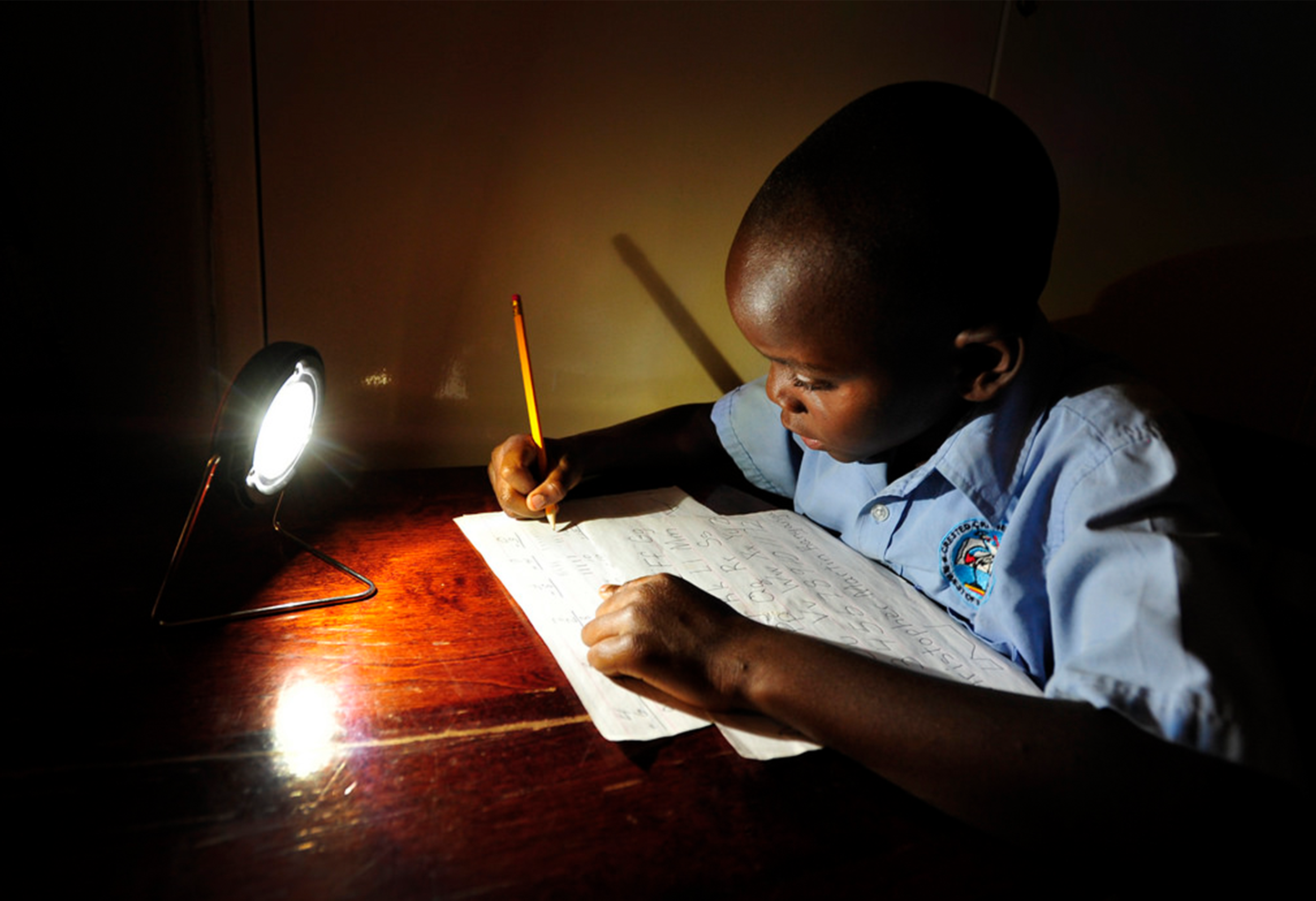
Rural electrification, the process of bringing electricity to remote and rural areas without access to it, is crucial to support the socio-economic development of communities and improve their living conditions.
Indeed, rural electrification generates the following effects:
- Increase in educational achievement, through allowing young people to study early in the morning or late at night.
- Greater efficiency and productivity, allowing businesses to be open longer hours and farmers to have access to equipment and techniques that improve their productivity, such as irrigation, processing, or food preservation.
- Job creation, directly or indirectly.
- Healthcare improvements, through improved lighting; possibility for storage and cooling of vaccines, blood and medicines; and equipment, such as X rays or ultrasound scanners.
- Improvement of security and safety, notably through street lighting and lit road signs.
- Reduction of isolation and marginalization through telephone lines, television, and radio.
- Reduction of the use of kerosene lamps and of indoor open fires used for cooking, as well as other polluting equipment.
- Reduction of gender-based violence occurring during the collection of firewood in remote areas.
The biggest challenge for rural electrification is the extension of grid electricity, which presents constraints such as high costs involved in reaching remote areas, higher costs of use than in urban areas, and power efficiency. Therefore, off-grid technologies, and notably solar mini-grids, offer a promising alternative.
Rural Electrification facts
- Among the 1.4 billion people without access to electricity, 85% are living in rural areas.
- According to the WHO, each year about 4 million people die from illnesses attributed to household air pollution from cooking stoves fuelled by biomass, kerosene and coal.
- In 2014, rural communities in India gained over US$20 million from increased economic activity driven by electrification.

NTU’s involvement in rural electrification
Through its rural electrification projects, NTU is committed to support in the achievement of the above-mentioned rural electrification positive results. We particularly contribute to reducing poverty, notably fuel poverty, and to increasing communities’ well-being. That is why we deliver diverse services in this field such as: elaboration of pre-feasibility and feasibility studies for innovation rural electrification solutions (including hydro plants, small and medium-sized wind turbines, solar photovoltaic plants); design, implementation and monitoring of mini-grid projects; elaboration of guidelines for mini-grid operations; development and implementation of new policies; strategies and programmes for access to energy in rural areas; improvement of rural electrification authorities’ planning, transparency and management systems; capacity development of rural electrification authorities and private developers in technical rural electrification areas.
NTU also supports access to clean energy solutions for rural development, notably through development and implementation of off-grid renewable energy schemes in rural areas.
Lastly, NTU is very committed to support rural communities in developing countries by proposing innovative solutions, such as electricity cooperatives or micro-financing, and by supporting the construction of resilient infrastructure in rural areas. The aim is to contribute to sustainable development while improving populations’ living conditions.